BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering cover DC and AC circuits, magnetic circuits, transformers, electrical machines, and basic electronics including logic gates and BJTs.
Unit-I BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering
ID.C. Circuits: Voltage and current sources, dependent and independent sources, Units and dimensions,
Source Conversion, Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Law, Superposition theorem, Thevenin’s theorem and their
application for analysis of series and parallel resistive circuits excited by independent voltage sources, Power
& Energy in such circuits. Mesh & nodal analysis, Star Delta transformation & circuits.
Unit-II BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering
1- phase AC Circuits: Generation of sinusoidal AC voltage, definition of average value, R.M.S. value, form
factor and peak factor of AC quantity , Concept of phasor, Concept of Power factor, Concept of impedance
and admittance, Active, reactive and apparent power, analysis of R-L, R-C, R-L-C series & parallel circuit
3-phase AC Circuits: Necessity and advantages of three phase systems, Meaning of Phase sequence,
balanced and unbalanced supply and loads. Relationship between line and phase values for balanced star and delta connections. Power in balanced & unbalanced three-phase system and their measurements
Unit-III BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering
Magnetic Circuits: Basic definitions, magnetization characteristics of Ferro magnetic materials,
self inductance and mutual inductance, energy in linear magnetic systems, coils connected in series, AC
excitation in magnetic circuits, magnetic field produced by current carrying conductor, Force on a current
carrying conductor. Induced voltage, laws of electromagnetic Induction, direction of induced E.M.F.
Single phase transformer: General construction, working principle, e.m.f. equation, equivalent circuits,
phasor diagram, voltage regulation, losses and efficiency, open circuit and short circuit test
Unit-IV BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering
Electrical Machines: Construction, Classification & Working Principle of DC machine, induction machine
and synchronous machine. Working principle of 3-Phase induction motor, Concept of slip in 3- Phase
induction motor, Explanation of Torque-slip characteristics of 3-Phase induction motor. Types of losses
occurring in electrical machines. Applications of DC machine, induction machine and synchronous machine.
Unit-V BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering
Basic Electronics: Number systems & Their conversion used in digital electronics, De morgan’s theorem,
Logic Gates, half and full adder circuits, R-S flip flop, J-K flip flop. Introduction to Semiconductors, Diodes,
V-I characteristics, Bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and their working, introduction to CC, CB & CE
transistor configurations, different configurations and modes of operation of BJT.
Course outcomes
The final outcome of the subject will result into an enhancement in understanding the basic concepts of Core
Electrical Engineering subjects. The topics covered under this subject will help to enhance the basic
understanding of Electrical machines and power systems and basic electronics.
Evaluation: Evaluation will be continuous and integral part of the class followed by final examination.
List of experiments
- Basic safety precautions. Introduction and use of measuring instruments – voltmeter, ammeter, multi-meter, oscilloscope. Real-life resistors, capacitors and inductors.
- Measuring the steady-state and transient time-response of R-L, R-C, and R-L-C circuits to a step change in voltage (transient may be observed on a storage oscilloscope). Sinusoidal steady state response of R-L, and R-C circuits – impedance calculation and verification. Observation of phase differences between current and voltage. Resonance in R-L-C circuits.
- Transformers: Observation of the no-load current waveform on an oscilloscope (non- sinusoidal wave-shape due to B-H curve nonlinearity should be shown along with a discussion about harmonics). Loading of a transformer: measurement of primary and secondary voltages and currents, and power.
- Determination of equivalent circuit parameters of a single phase transformer by O.C. and S.C. tests and estimation of voltage regulation and efficiency at various loading conditions and verification by load test.
- Demonstration of cut-out sections of machines: dc machine (commutator-brush arrangement), induction machine (squirrel cage rotor), synchronous machine (field winging – slip ring arrangement) and single-phase induction machine.
- Torque Speed Characteristic of separately excited dc motor.
- Synchronous speed of two and four-pole, three-phase induction motors. Direction reversal by change of phase-sequence of connections. Torque-Slip Characteristic of an induction motor. Generator operation of an induction machine driven at super- synchronous speed.
- Synchronous Machine operating as a generator: stand-alone operation with a load. Control of voltage through field excitation.
- Study of V-I Characteristics of Diodes.
- Applications of Diodes and their verification.
- Transistor applications as amplifier and switch.
- Verification of truth table for various gates, Flip-Flops.
- Realizations of Various gates, Flip-Flops etc.
- Verification of De morgan’s theorems.
References
- D.P. Kothari & I.J. Nagrath, Basic Electrical Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill, latest edition.
- S.N. Singh , Basic Electrical Engineering, P.H.I.,2013
- Rajendra Prasad, Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, Prentice Hall,2014
- M.S. Sukhija, T. K. Nagsarkar, Basic Electrical and electronics engineering, Oxford University
press,2012. - C.L. Wadhwa, Basic Electrical Engineering. New Age International.
- B.L. Theraja & A.K Theraja Textbook of Electrical Technology – Vol. 1, S. Chand Publication.
- E. Hughes & I.M. Smith Hughes Electrical Technology Pearson.
- Vincent Del Toro Electrical Engineering Fundamentals.
Important Questions of BT-104 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering
Q1. Stateand explain Kirchhoff’s current and voltage law.
Q2. State and explain Superposition theorem.
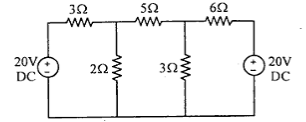
Q3. Find the current through 5-ohm resistance shown in fig using mesh current analysis.
Q4. Define the following with respect to alternating quantity.
- RM.S. value
- Peak value
- Average value
- Instantaneous value
Q5. Explain Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
Q6. Explain the role of resistance, capacitance and inductance in an electric circuit.
Q7. Explain the working principle of a single-phase transformer.
Q8. In a 25 kVA, 2000/200 power transformer the iron and copper losses are 350W and 400W respectively. Calculate the efficiency at full load.
Q9. Explain with schematic diagram different parts of D.C. machines.
Q10. Explain the principle of three phase induction motor.
Q11. Draw and explain the V-I characteristic of diode.
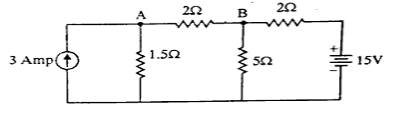
Q12. Find the value of current in branch AB by using Super position Theorem.
Q13. What do you understand by dependent and Independent sources? Explain with neat sketches. How we can convert a Voltage source into a current source?
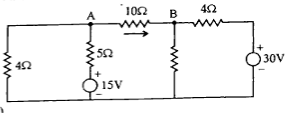
Q14. Using Nodal Analysis, find the current through the 10Q resistor in the figure shown below.
Q15. Define the average value, RMS value form factor, and peak factor of an AC quantity. How are these parameters calculated for a sinusoidal waveform?
You Should also read this:
RGPV First Year Syllabus of BT-102 Mathematics-I
RGPV Syllabus of BTech First Year BT-101 Chemistry
RGPV First Year Syllabus and Important Questions of BT-103 English for Communication
Visit official website of RGPV for more information: Click here
